

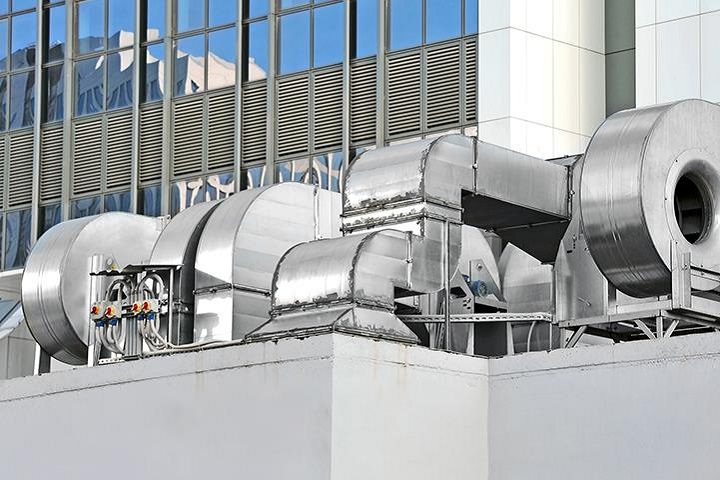

Central Air Conditioners (HVAC)
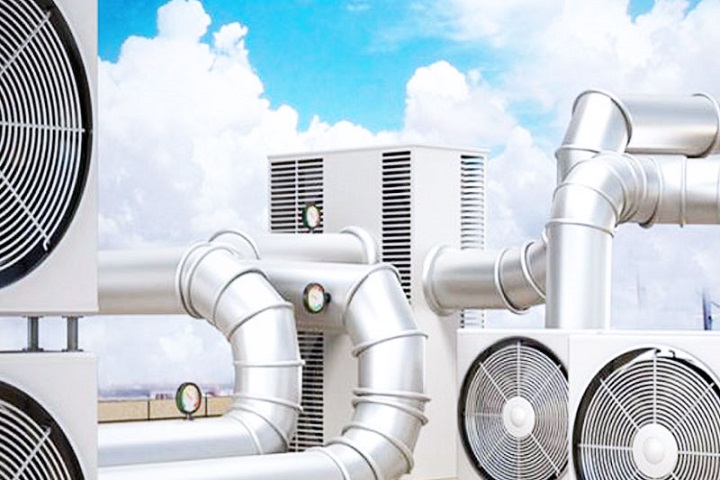
Central air conditioners, also known as HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) systems, are used to cool and dehumidify the air in a building or home. They work by using a refrigeration cycle to transfer heat from inside the building to the outside.
The process begins when warm air is drawn into the air handler unit (AHU) through the return air ducts. The air passes over the evaporator coil, which is filled with a cold refrigerant. The refrigerant absorbs heat from the air, causing the air to cool and release moisture, which is collected in a condensate pan and drained away.
The cooled and dehumidified air is then sent back into the building through the supply air ducts. The warm refrigerant then passes through a compressor, which compresses it into a high-pressure gas. The gas then flows through a condenser coil, which is located outside the building.
As the refrigerant passes through the condenser coil, it releases heat into the outdoor air, causing the refrigerant to cool and condense back into a liquid. The liquid refrigerant then flows back into the AHU, where the process begins again.
Central air conditioners require regular maintenance, including cleaning or replacing air filters, checking refrigerant levels, and inspecting electrical connections. Proper maintenance can ensure that the system operates efficiently and effectively, providing cool, comfortable air for years to come.
